Resistance to any particular product or class of product is developed when the same MOA product is used for a prolonged period , to maintain efficacy farmers need to use active ingredients diligently at all times. We continue to explore in developing new combinational products, with broad spectrum and multimodal effect to target the pest and disease. We strongly focus on product stewardship from developing effective formulation and keep looking ways of improving the efficiency throughout its life cycle keeping sustainability, care for the environment, beneficial insects and farmers.

Integrated Control Strategies
Incorporate as many different control strategies as possible including the use of synthetic insecticides, biological insecticides, beneficial insects (predators/parasites), cultural practices, transgenic plants (where allowed), crop rotation, pest-resistant crop varieties and chemical attractants or deterrents.
Applications of insecticide must be timed correctly, targeting the most vulnerable life stage of the insect pest. The use of spray rates and application intervals recommended by the manufacturer and in compliance with local agricultural extension regulations is essential.
It is important to mix and apply insecticides carefully. As resistance increases, the margin for error in terms of insecticide dose, timing, coverage, etc., assumes even greater importance. Recommendations from manufacturers and local advisors should be followed.
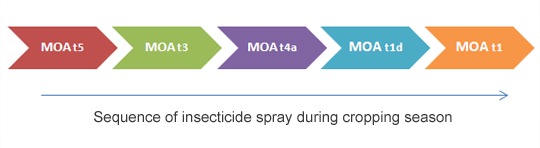
A key element of effective resistance management is the use of alternations, rotations, or sequences of different insecticide MoA classes. Users should avoid selecting for resistance or cross-resistance by repeated use within the crop cycle, or year after year, of the same insecticide or related products in the same MoA class
It is important to consider the impact of pesticides on beneficial insects, and use products at labeled rates and spray intervals to minimize undesired effects on parasitoids and predators.
Preserve susceptible genes. Some programs try to preserve susceptible individuals within the target population by providing a refuge or haven for susceptible insects, such as unsprayed areas within treated fields, adjacent refuge fields, or attractive habitats within a treated field that facilitate immigration. These susceptible individuals may out-compete and interbreed with resistant individuals, diluting the impact of any resistance that may have developed in the population.
Consider crop residue options. Destroying crop residues can deprive insects of food and overwintering sites. This cultural practice will kill pesticide-resistant pests (as well as susceptible ones) and prevent them from producing resistant offspring for the next season. However, farmers should review their soil conservation requirements before removing residues.

Proplan-PE is a product developed specially for fruit trees to improve the plants flowering and fruit setting. PROPLAN PE contains polysaccharines, proteins, polypeptides, amino acids

Proplan-VG is a product developed specially for fruit trees to improve the plants flowering and fruit setting. PROPLAN -VG contains polysaccharines, proteins, polypeptides, amino acids

vivast™ is a proprietary unique range of products based on advanced polymerization technique of Poly D-Gulosamine non-toxic biodegradable polymer that combines a unique set

expon™ a premix insecticide Thiamethoxam 14.6% + Lambda-cyhalothrin 10.1% SC gives an exponential control by delivering multi modes of action against the target pest